26 Sourcing Terms You Should Know In The Beverage Industry

Identifying, negotiating, and purchasing all of the elements that go into a beverage takes skill and an in-depth understanding of several different industries and the terms that go along with each. Here are a few sourcing terms that beverage entrepreneurs should know.
Barrel
A barrel is a round vessel of greater length than breadth and bulging in the middle with flat ends or heads. A barrel is usually made of staves (wooden planks) bound with hoops and has flat ends or heads. Barrel can also refer to a similar cylindrical container made of metal, usually called a drum. A barrel is also a unit of volume with a fixed amount for a certain commodity. The abbreviation for barrel is bbl. Barrels typically range in capacity from 50-55 gallons.
BOM
A bill of materials (BOM) is a list of the raw materials and the quantities of each needed to manufacture an end product.
Can Artwork Trapping
Trapping is a method of adjusting areas where two distinct, adjacent colors meet so that press misregistration won't cause white spaces. If you knock out graphics or type you may have to create a trap to ensure that you don't have white spaces due to misregistration.
Dieline
A dieline is used in graphic design as a placeholder for assisting in the proper layout of a document that will be diecut as part of the finishing process. It is usually placed into the graphic's computer file as a separate layer for sizing and orientation purposes. A dieline is usually not printed on the final piece but is used to determine correct layout.
Drum
A drum is a cylindrical container used for shipping bulk cargo. Drums can be made of steel, dense paperboard (commonly called a fiber drum), or plastics, and are generally used to transport and store of liquids and powders. Drums are also commonly called barrels. Although the standard drum holds between 50 and 55 gallons, the fill can vary. Certain juices will fill a 55-gallon drum with 48 gallons of liquid.
Extract
An extract is a substance made by extracting a part of a raw material, often by using a solvent such as ethanol or water. Extracts are sold as tinctures, liquid or in powder form.
HACCP
Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) is a management system that addresses food safety through the analysis and control of biological, chemical, and physical hazards from raw material production, procurement and handling, to manufacturing, distribution and consumption of the finished product. The HACCP process helps to systematically prioritize and control hazards as well as to identify where and how these hazards might occur.
High Intensity Sweeteners
High Intensity Sweeteners are ingredients used as sugar alternatives because they are many times sweeter than sugar but contribute few or no calories. High intensity sweeteners are chosen in place of sugar because they only contribute a few calories and generally will not raise blood sugar levels.
Intermediate Bulk Containers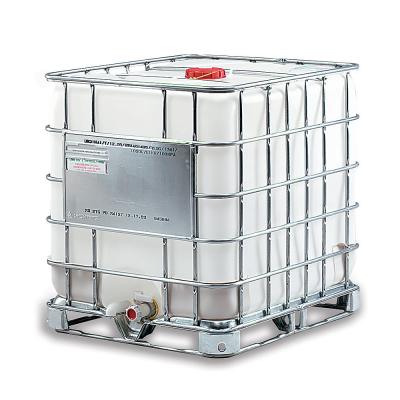
Intermediate Bulk Containers (IBC) – also known as IBC totes, IBC tank, or pallet tanks – are reusable, multi-use industrial containers that have been engineered for the mass handling, transport and storage of liquids, pastes or solids. The two main categories are flexible (FIBC) and rigid IBCs
ISO Certification
 ISO certifications are designed to ensure that the products, services and process a company uses conform to acceptable international standards. The most common certifications are the ISO 9000 family of standards, which are designed to ensure that products and services are of high quality and are always being improved. In 2018, the current version is ISO 9001:2015, which can be used by any business. ISO 9001:2015 deals with eight primary business principles: customer focus, leadership, involvement of people, process approach, system approach to management, continual improvement, factual approach to decision making, and mutually beneficial supplier relationships.
ISO certifications are designed to ensure that the products, services and process a company uses conform to acceptable international standards. The most common certifications are the ISO 9000 family of standards, which are designed to ensure that products and services are of high quality and are always being improved. In 2018, the current version is ISO 9001:2015, which can be used by any business. ISO 9001:2015 deals with eight primary business principles: customer focus, leadership, involvement of people, process approach, system approach to management, continual improvement, factual approach to decision making, and mutually beneficial supplier relationships.
Lead Time
Lead Time is the time between the placement of an order and delivery.
MOQ
MOQ is an acronym which stands for Minimum Order Quantity and refers to the minimum amount of a commodity that can be ordered from a supplier. MOQs can be quoted in dollars or in units.
MSDS
The material safety data sheet (MSDS) is a document that lists information relating to occupational safety and health for the use of various substances. MSDSs are a widely used system for cataloging information on chemicals, chemical compounds, and chemical mixtures. MSDS information may include instructions for the safe use and potential hazards associated with a particular material or product, along with spill-handling procedures. MSDS formats can vary from source to source within a country depending on national requirements. An MSDS for a substance is not primarily intended for use by the general consumer, focusing instead on the hazards of working with the material in an occupational setting. The MSDS is also referred to as the Safety Data Sheet (SDS).
Packaging Configuration
Packaging Configuration, commonly referred to a “pack-out,” refers to the combination in which the sell-able product is arranged with both primary and secondary packaging. The most common pack-outs are 12 or 24 loose in a tray, two 12-packs, four 6-packs, and six 4-packs.
Pail
As a technical shipping term, pail is used to designate a type of cylindrical shipping container with a capacity of about 1 to 12 gal (3 to 50 L). It can have straight or slanted sides and usually has a handle or bail. The 5-gallon pail (40 lbs) is the most commonly used size. Some suppliers will further break down capacity using jugs or cartons.
Primary Packaging
Primary packaging is the layer of packaging that is in immediate contact with the liquid. Examples of primary packaging include cans, glass bottles and plastic bottles.
PSL
Pressure Sensitive Labels (PSLs) require pressure to form a bond between the adhesive and the product. No water, solvent or heat is needed for the label to stick to the product. PSLs can the can be easily applied and easily removed. Pressure sensitive labels consist of a face stock and adhesive. They are printed and delivered in roll form and can come in a variety of materials, colors and sizes.
PETG
Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG) is a type of plastic used in bottles and shrink sleeves and labels. It is a clear material that is designed to be easy to use in a range of applications. PTEG has an excellent chemical resistance, is easily thermoformable. It is also sterile and recyclable. PETG fabricates well throughout a number of different processes including cutting, drilling, bending, routing and polishing. It’s also possible to silk screen PETG using various inks. It also bonds well with solvents or adhesives. Due to its low forming temperature, PETG can be easily vacuum or pressure-formed and bent by heat.
PVC
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a type of plastic used in bottles and shrink sleeves. PVC is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer, after polyethylene and polypropylene.
RDA
Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) is the daily dietary intake level of a nutrient considered sufficient by the Food and Nutrition Board of the Institute of Medicine to meet the requirements of 97.5% of healthy individuals in each life-stage and sex group.
RSC
Regular Slotted Container (Corrugated) is typically called a “Master Shipper” in bottle secondary packaging. The RSC is the most common box style. All of the flaps have the same length, and the two outer flaps are one-half the container's width, so they can meet in the center. The flaps require glue, tape, or staples to close. The efficient design of the RSC ensures that there is little manufacturing waste.
Secondary Packaging
Secondary packaging is the layer of packaging that surrounds groups of the primary packaging, bundling and protecting the primary package grouping. Trays and cartons are examples of secondary packaging.
SUS Board
SUS stands for Solid Unbleached Sulfate. Some manufacturers call it Coated Natural Kraft® – CNK® (Westrock) or Coated Unbleached Kraft -CUK (Graphic Packaging). The 100% virgin fiber is unbleached but the board comes with a thick coating on one side for an outstanding color rendering. Its natural resistance to moisture make it ideal for refrigerated and frozen applications.
Tanker
A tanker is a container designed to transport or store liquids or gases in bulk. A tanker’s capacity generally ranges between 5,000-6,000 gallons.
Thermochromic Inks
Thermochromic inks change hues in response to temperature fluctuations. Companies use these inks to help capture consumers' attention and differentiate their brand. The two major categories of thermochromic inks are thermochromatic liquid crystals (TLCs) and leuco dyes. Leuco dyes are generally more cost effective and don't interfere with recycling. Beer and energy drink companies are known for incorporating temperature-sensitive graphics into their products. Leuco dyes don't interfere with recycling.
WPG
Weight per gallon (WPG) is the measure of density of a liquid. A gallon of water weighs 8.34 pounds, making the density 8.34 pounds/gallon. Density varies with temperature. The TTB uses densities at 60 degrees Fahrenheit.
There's a lot to know about beverage souring and supplier management. The most important thing to remember is that you're not alone. BevSource specializes in helping beverage entrepreneurs develop, produce, and deliver their beverage ideas to the world. Give us a call!
Looking to learn more?
